Molecular Landscape of Cases with Borderline HbA2 Levels in a Malaysian Tertiary Medical Centre
Plateletpheresis Effects on Blood Parameters
Abstract
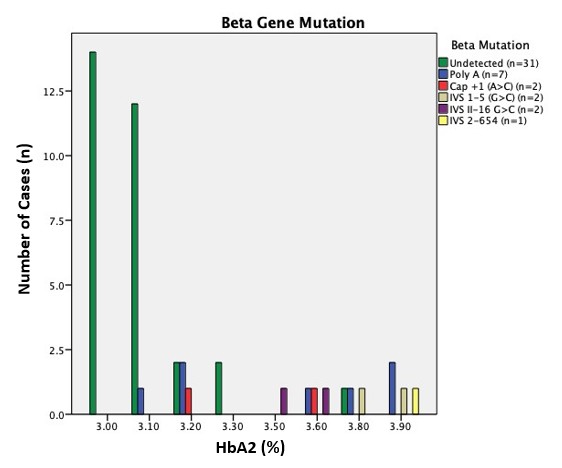
Thalassaemia is a prevalent genetic disease in Malaysia affecting up to 6% of the population. A rise in haemoglobin A2 (HbA2) of more than 4% is among the most important parameters for identification of β-thalassaemia carriers. However, some cases with the HbA2 levels in the borderline range between 3.0% to 3.9% has been shown to harbour α-, β-globin and/or Krüppel-like factor 1 (KLF1) gene abnormalities too. Here, we reported the results of molecular investigations on a group of subjects with borderline HbA2. A total of 45 subjects with borderline HbA2 levels in Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz (HCTM) were identified from the hospital information system. Data of their full blood count using Sysmex XN-1000, and haemoglobin quantitation using Sebia Capillary Variant II were collected. Their DNA were investigated for the presence of locally common pathological mutations in the β-globin gene, deletions of the α-globin gene as well as screened for KLF1 gene mutation. This study found that 44% of the cases with borderline HbA2 in HCTM showed genetic abnormality at the molecular level comprising of β-globin gene mutation (29%), α-gene defect (9%), KLF1 gene abnormalities (4%) and coinheritance of α- and β-gene defect (2%). On the basis of our findings, we strongly suggest molecular methods consisting of β- and α-globin genes study to be considered in the investigation for haemoglobinopathies in the borderline HbA2 group of patients. Further study on KLF1 gene mutation test in our population is recommended to further characterise the common mutations of the gene.
Keywords :
Borderline HbA2; KLF1 gene; thalassaemia,
Abstrak
Talasemia merupakan penyakit genetik yang lazim di Malaysia dan menjejaskan sehingga 6% daripada populasi. Peningkatan paras hemoglobin A2 (HbA2) melebihi 4% merupakan salah satu parameter penting dalam mengenal pasti pembawa talasemia β. Namun begitu, terdapat juga kes dengan paras HbA2 pada julat sempadan antara 3.0% hingga 3.9% yang dikesan mempunyai keabnormalan pada gen α-, β-globin dan/atau Krüppel-like factor 1 (KLF1). Kajian ini melaporkan hasil penyiasatan molekul terhadap sekumpulan subjek dengan paras HbA2 sempadan. Seramai 45 subjek dengan paras HbA2 sempadan di Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz (HCTM) dikenal pasti melalui sistem maklumat hospital. Data kiraan darah penuh menggunakan Sysmex XN-1000 dan kuantifikasi hemoglobin menggunakan Sebia Capillarys 2 dikumpulkan. DNA subjek dianalisis bagi mengesan mutasi patologi gen β-globin yang lazim di Malaysia, penghapusan gen α-globin serta mutasi gen KLF1. Kajian ini mendapati bahawa 44% daripada kes HbA2 sempadan di HCTM menunjukkan keabnormalan genetik di peringkat molekul yang merangkumi mutasi gen β-globin (29%), kecacatan gen α-globin (9%), keabnormalan gen KLF1 (4%) dan pewarisan bersama kecacatan gen α dan β (2%). Berdasarkan penemuan ini, kami mencadangkan agar kaedah molekul yang melibatkan kajian gen β- dan α-globin dipertimbangkan dalam penyiasatan hemoglobinopati bagi pesakit dengan HbA2 sempadan. Kajian lanjut mengenai mutasi gen KLF1 juga disarankan untuk mencirikan mutasi lazim gen tersebut dengan lebih terperinci.
Kata Kunci :
Gen KLF1; julat sempadan HbA2; thalassaemia,
Correspondance Address
Hafiza Alauddin. Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Jalan Yaacob Latiff, Bandar Tun Razak, 56000 Cheras, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Tel: +603-91455373 Email: drhafiza@hctm.ukm.edu.my